How to maintain weight loss after a low-calorie diet?
Transitioning from a Low-Calorie Diet
One of the most critical phases of weight loss maintenance is transitioning from a strict low-calorie diet to a more sustainable eating pattern. This is a phase that largely decides how successful your weight loss journey will be in the long run. It's crucial to understand that the process should be gradual and meticulously planned. Let's delve into a more detailed step-by-step guide for making this transition smoothly and effectively.
Gradually Increasing Calorie Intake
Upon reaching your weight loss goal with a low-calorie diet, you might wonder, 'What’s next? Can I slide back into my old eating habits?' The answer is to find a middle ground. Returning to a high-calorie diet will lead to weight gain, but maintaining a low-calorie diet in the long run isn't optimal either due to potential nutritional deficiencies.
Thus, your goal should be increasing your calorie intake gradually. Instead of adding an extra meal all of a sudden or dramatically increasing the portion sizes, make small changes every day. For example, add an additional healthy snack to your daily routine or slightly increase the portion size of your meals. Over time, these small changes will result in a sustainable increase in your calorie intake whilst maintaining your weight.
Balancing Macronutrients
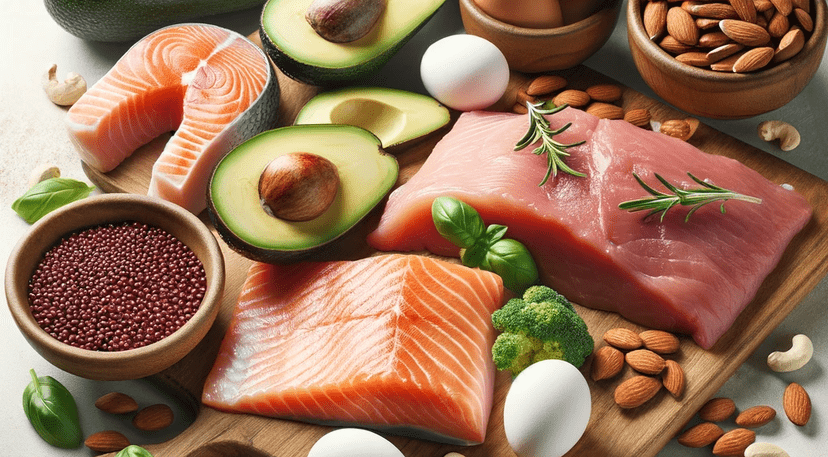
A major part of this transition involves balancing macronutrients in your meals. Macronutrients, the nutritional building blocks of our diet, consist of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. A balanced combination of these is crucial to maintain optimal health and preserve the weight loss.
It's important to incorporate an adequate amount of each macronutrient into your meals. For instance, ensure that your diet contains enough protein, which aids in satiety and can reduce the temptation to overeat. Include healthy fats, such as avocado and nuts, which are also satiating and beneficial for your overall health.
Carbohydrates, while often labeled as weight gain culprits, are also an essential part of a balanced diet. Choose complex carbohydrates (such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables) instead of simple ones (like white bread, pasta, and sweets). These complex carbs are digested slowly and keep you full longer, helping you to avoid unnecessary snacking.
Understanding Your Body's Signals
Finally, understanding your body's signals plays an indispensable role in maintaining your weight after a low-calorie diet. Your body sends you cues about hunger and satiety that are vital to comprehend and respond to appropriately to avoid overeating and experience healthy weight control.
When you're genuinely hungry, your body needs nutrients. Ignore these signals, and you might overeat later. On the other hand, you might mistake boredom, thirst, or emotional distress as hunger. Are you eating because your body needs fuel, or are you succumbing to a craving or emotional eating?
Understanding these vital signals helps tailor your eating pattern to suit your body's needs truly and maintain your weight loss. Listen to your body, learn to differentiate between real hunger and cravings, and respond with nourishing food choices.
In conclusion, transitioning from a low-calorie diet to a sustainable eating pattern takes time and involves gradual increases in calorie intake, balancing macronutrients, and understanding your body's signals. By taking these practical steps, you can sustain the weight loss you've worked hard to achieve and embark on a lifelong journey of healthy eating.
Developing a Sustainable Eating Habit
Maintaining weight loss after a diet is key and much relies on taking the right steps towards developing a sustainable eating habit. This guide will delve into the various aspects of long-term healthy eating, with particular emphasis on regular meal patterns, mindful eating, and the incorporation of nutrient-dense foods.
Establishing Regular Meal Patterns
A consistent eating schedule is essential for successful weight maintenance after a diet. Regular meal patterns not only help to curb excessive hunger but also moderate your metabolism, enable better digestion, and enhance nutrient absorption. They act as a barrier against overeating, a significant challenge when transitioning from a diet to a more sustainable eating pattern.
When you cease a low-calorie diet plan, it's essential to establish a regular pattern of meals spaced throughout the day. Ideally, you should eat every three to four hours, incorporating three nourishing meals a day with healthy snacks in between. This regularity can support satiety and help to regulate your blood sugar levels, avoiding sharp spikes and crashes that can lead to cravings and overeating.
Choosing Nutrient-Dense Foods
Incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods is another crucial aspect of sustainable eating. Nutrient-dense foods are typically high in vitamins, minerals, complex carbohydrates, lean protein, healthy fats, and fiber, but low in calories. Examples include whole grains, lean meats, fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
Eating a diverse range of nutrient-dense foods not only provides the body with the necessary energy and nutrients for optimal function, but also keeps your meals exciting and satisfying. Opting for whole foods over processed ones aids in maintaining a healthier body weight and enhancing overall well-being. Introducing this variety helps to ensure that your body receives an adequate supply of essential nutrients and prevents the monotony that often leads to unhealthy food choices.
Practicing Mindful Eating
Mindful eating is an approach that involves paying full attention to the experience of eating and drinking, both inside and outside the body. This practice encourages an awareness of the food's tastes, smells, and textures, and the body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Practicing mindful eating makes you more tuned into your body's signals, helping you recognize when you're truly hungry and when you're satisfied. It encourages slower, more thoughtful eating and has been shown to aid in weight control. Here's how to practice mindful eating:
- Sit at a table dedicated to eating, without distractions like television or smartphones.
- Appreciate your food, taking time to consider the effort that went into its production and preparation.
- Eat slowly, taking smaller bites, chewing thoroughly, and savoring the moment.
Developing a sustainable eating habit post-diet involves establishing a rhythm of regular meals, opting for nutrient-rich food, and incorporating mindful eating. Comprehensive application of these principles serves not only the purpose of weight maintenance but extends far into overall health improvement.
Incorporating Physical Activity and Lifestyle Changes
After achieving your desired weight loss with a low-calorie diet, the next challenge is to maintain that weight loss. One of the crucial methods to sustain your current weight level is through the incorporation of physical activity and adoption of healthy lifestyle changes. Indeed, these two factors work synergistically to not only keep the pounds off but also enhance overall health and wellness.
Finding the Right Exercise Routine
Physical activity plays an instrumental role in maintaining weight loss. It's a fact backed by numerous scientific studies that show a positive correlation between sustained weight loss and regular exercise. One such research, published in the Journal of Obesity, disclosed that successful weight maintenance was linked with higher levels of physical activity.
Subjecting your body to regular exercise helps to increase your metabolic rate, which is the rate at which your body burns calories. This metabolic boost helps maintain a balance in your energy equation (calories in vs. calories out), which is intrinsic in maintaining your weight after a low-calorie diet.
While this may sound intimidating, exercise does not necessarily mean spending countless hours in the gym. The goal here is to find an exercise routine that fits into your lifestyle. This routine could be anything from brisk walking, cycling, swimming, weight lifting, yoga, or dance classes. The important part is that you engage in exercise that you enjoy.
Managing Stress and Emotional Eating
Another vital aspect of lifestyle change lies in managing your mental health. There’s a common misconception that weight maintenance is solely about diet and exercise when, in truth, psychological well-being proves just as significant.
High levels of stress have been linked with an increase in cortisol production, popularly known as the 'stress hormone.' Elevated cortisol levels can instigate emotional eating and increase cravings for junk food. Therefore, managing stress and emotional eating is integral in maintaining the fruits of your low-calorie diet.
To help you manage stress and emotional eating, you may consider methods such as:
- Regular mindfulness or meditation practices
- Talking to a therapist or counselor
- Employing stress reduction techniques like deep breathing or yoga
Ensuring Adequate Sleep
Finally, make no mistake, adequate sleep is equally important in the weight maintenance journey. A research paper published in the Annals of Internal Medicine noted that inadequate sleep could thwart weight loss efforts because it alters the body's hormone levels, leading to increased hunger and less satiety.
Consistently getting a proper night’s sleep (about 7-9 hours for adults) can help regulate these hormones and thus minimize overeating risks. Besides, during sleep, the body also performs various metabolic and recovery processes, making it an essential factor for general health, beyond weight maintenance.
Now you better understand how essential it is to incorporate physical activity and lifestyle changes for long-term weight maintenance. Remember, this is a continuous journey, and it's crucial to be patient with yourself along the way.
With proper measures for maintaining physical fitness, reduced stress levels, emotional well-being, and sufficient sleep, you're better equipped to sustain your weight loss results aside your low-calorie diet.
In Summary
To recap, this blog post discusses valuable strategies involving dietary adjustments, physical activity, and lifestyle changes to transition from a low-calorie diet to a sustainable lifestyle for long-term weight maintenance.
-
Gradually Increasing Calorie Intake: A planned increment in calorie intake helps maintain the attained weight loss without leading to nutritional deficiencies.
-
Balancing Macronutrients: Balancing the intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is critical for optimal health and weight maintenance.
-
Understanding Your Body's Signals: Recognizing and appropriately responding to your hunger and satiety cues prevents overeating and facilitates weight control.
-
Establishing Regular Meal Patterns: Regular meal times aid in curbing excessive hunger, moderating metabolism, and enhancing nutrient absorption.
-
Choosing Nutrient-Dense Foods: Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods boosts nutrient intake and adds variety to your meals.
-
Practicing Mindful Eating: Being mindful during eating can improve your understanding of your body's needs, help control portion sizes, and enhance digestion.
-
Finding the Right Exercise Routine: Regular physical activity boosts metabolism and helps maintain weight loss.
-
Managing Stress and Emotional Eating: Maintaining mental health is crucial for preventing emotional eating and managing weight.
-
Ensuring Adequate Sleep: Adequate sleep is vital for hormonal regulation, preventing overeating, and overall health.
Plan of Action
To implement the strategies discussed:
-
Gradually Increase Caloric Intake:
- Make a plan to increase your calorie intake incrementally.
- Start by adding healthy snacks or slightly larger portion sizes to your meals.
-
Balance your Macronutrients:
- Examine your current diet and adjust where necessary to ensure a balance of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
-
Understand your Body's Signals:
- Pay more attention to your hunger and satiety signals and respond appropriately.
-
Establish Regular Meal Patterns:
- Plan your meals and snacks to occur at regular intervals throughout the day.
-
Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods:
- Aim to include a variety of nutrient-dense foods in your daily meals.
-
Practice Mindful Eating:
- Dedicate time and space solely for eating.
- Pay attention to the tastes, smells, and textures of your food.
-
Find a suitable Exercise Routine:
- Choose an exercise routine that aligns with your lifestyle and stay consistent.
-
Manage Stress and Emotional Eating:
- Develop a stress management strategy that includes activities like mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
-
Ensure Adequate Sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep every night to best support your health and weight maintenance.
Implementing these principles and action steps can make the journey towards sustainable weight maintenance smoother and more successful. Remember, this is your personal journey. Be patient and kind to yourself as you transition from a low-calorie diet to a healthier, sustainable lifestyle.
![Does a 400 and 600 Calorie Diet Plan Help Weight Loss?[ANSWERED]](https://img.imageboss.me/onestep/width/828/format:auto,quality:80/assets/site/blog/does-a-400-and-600-calorie-diet-plan-help-weight-loss.png)
![How Many Calories Does 10,000 Steps Burn? [ANSWERED]](https://img.imageboss.me/onestep/width/828/format:auto,quality:80/assets/site/blog/how-many-calories-does-10000-steps-burn.png)