Introduction to Bariatric Surgery
Renowned as a transformative approach to managing obesity, Bariatric Surgery is a set of procedures that aim to facilitate significant weight loss by surgically modifying the body's digestive system. Touted as one of the most effective weight loss strategies, it's not just about ridding the pounds but also about resolving or improving obesity-related conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
Healthcare practitioners often see it as the last resort when lifestyle modifications and pharmacologic treatment fail to gain the desired effects. As life-altering as it might seem, bariatric surgery is not for everyone. It has its specific set of criteria that need serious consideration.
Purpose and Goals of Bariatric Surgery
The primary purpose of bariatric surgery goes beyond weight reduction. This surgical intervention caters to those who have struggled with obesity, facing a higher risk for various health concerns. Bariatric surgery can significantly improve quality of life and longevity by controlling and in some cases completely resolving those worrisome co-morbid conditions.
Your physical health will see drastic improvements in areas such as cardiovascular wellbeing, blood sugar levels, sleep patterns, and more. Besides the direct physiological benefits, bariatric surgery can dramatically enhance psychological health by improving body image, social interactions, and overall self-esteem.
Criteria for Bariatric Surgery Candidates
As a substantial medical intervention, challenging both physically and psychologically, Bariatric Surgery has an established set of criteria in place. According to the National Institute of Health, potential candidates must have:
- A Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or more, which equates to being about 100 pounds overweight for men and 80 pounds for women.
- A BMI between 35 and 39.9 coupled with serious weight-related health problems like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or severe sleep apnea.
- Unsuccessful attempts at diet and lifestyle changes under professional guidance for weight loss.
A psychological evaluation is performed to ascertain emotional stability and understanding of the procedure's demands and effects.
Overview of the Weight Loss Mechanisms
Bariatric surgery facilitates weight loss in one or two primary ways: restriction and malabsorption.
- Restriction: Surgical procedures like sleeve gastrectomy and gastric banding reduce the stomach's size, which curbs your ability to consume food, causing a sense of fullness after eating small quantities.
- Malabsorption: Procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass modify your digestive system to cut down on the absorption of calories and nutrients from the consumed food.
Endeavoring to undertake bariatric surgery is by no means an easy choice. It demands unwavering commitment and fundamental changes to your lifestyle for it to bear the fruit of improved health and lifestyle.
Always remember, bariatric surgery is not a quick-fix for obesity, and it's not a substitute for healthy living. Instead, it sets a solid ground for someone to adopt permanent changes towards healthier eating habits, regular physical activity, and an overall balanced lifestyle. Rest assured, understanding the intricate details of each of these operations, and the lifestyle changes they demand, will provide you with comprehensive guidance to embark on this life-altering journey.
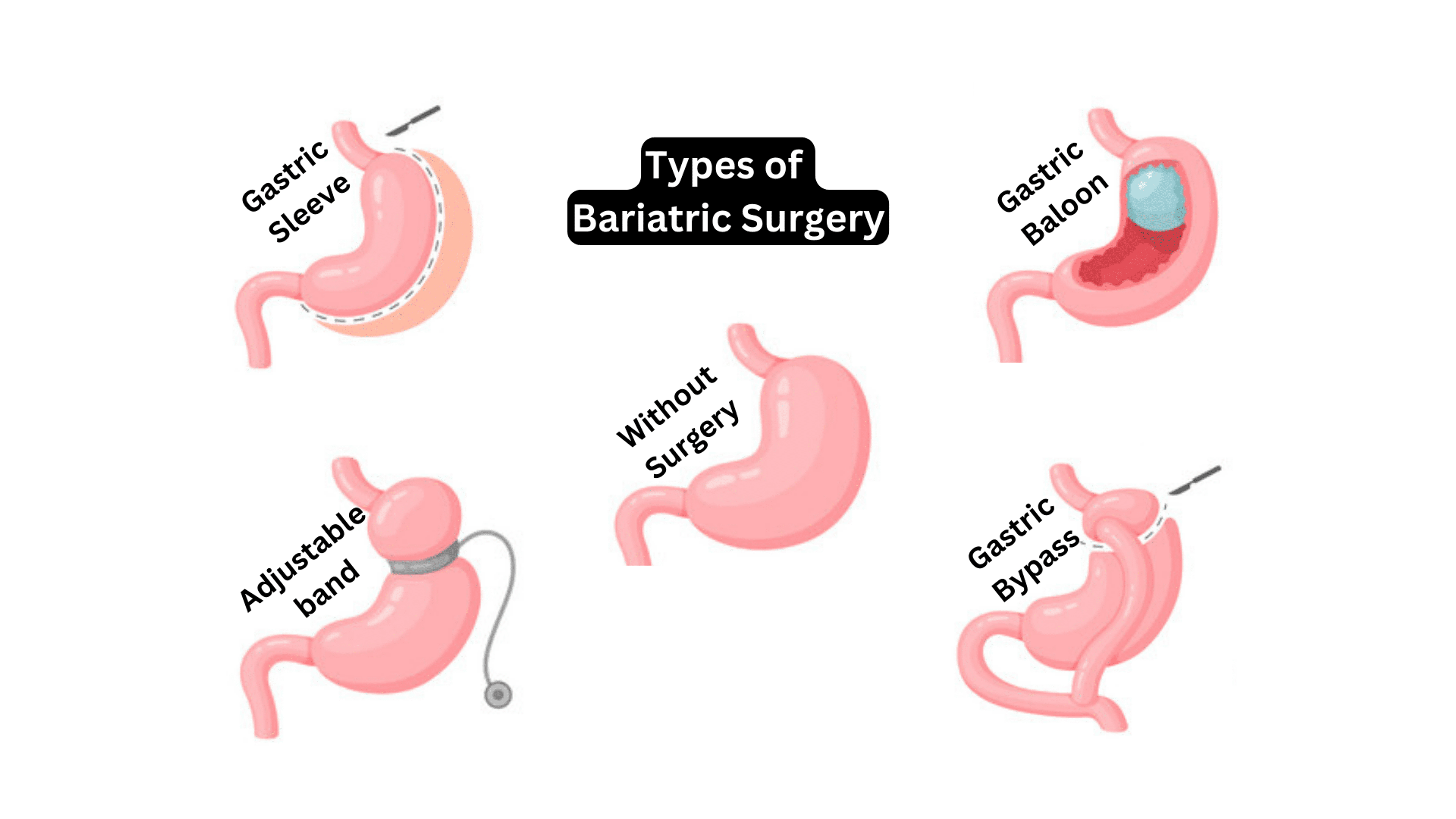
Common Types of Bariatric Surgery
As we delve into the world of bariatric surgery, you will find that there are several options available, each with its own set of benefits and potential risks. Our goal here is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the most common types, including Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric band, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch.
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Firstly, the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, commonly known as RYGB, is a well-established procedure in bariatric surgery. In this technique, a small pouch is created at the top of the stomach, which significantly limits the amount of food that can be consumed and reroutes part of the digestive system to cause malabsorption.
The benefits of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass include swift and substantial weight loss, significant improvement in obesity-related health conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, and improved quality of life overall. However, potential risks can involve significant dietary restrictions and potential malnutrition, along with the usual risks associated with any surgical procedure such as infection or bleeding.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Next, we have the sleeve gastrectomy. This process involves the removal of a large portion of the stomach, shaping the remaining part into a tube-like structure or "sleeve." This smaller stomach size promotes a feeling of fullness quicker and reduces the amount of food one can consume.
The benefits of sleeve gastrectomy include considerable weight loss and an improvement in many obesity-related health conditions. As this procedure does not affect the absorption of food, nutritional deficiencies are less likely as compared to gastric bypass. The risk factors are similar to those in other weight reduction surgeries, such as leakage from the line where parts of the stomach have been stapled together.
Adjustable Gastric Band
The adjustable gastric band technique, often referred to as a "lap band," includes placing an inflatable band around the upper portion of the stomach to create a small pouch and narrow passage into the rest of the stomach. This method limits the amount of food the stomach can hold and slows down digestion.
One of the critical advantages is that no part of the stomach or intestine is cut, and the procedure is reversible. However, the weight loss tends to be slower and lesser in comparison to other procedures. Additionally, the band may require adjustments or may lead to complications such as slipping or erosion into the stomach.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch
Finally, the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a complex procedure that involves removing a part of the stomach, similar to sleeve gastrectomy, and rerouting a significant part of the small intestine, creating two separate pathways and one common channel.
It is a powerful weight-loss method that allows eating considerably larger amounts of food than other procedures allow. There is a dramatic improvement in conditions such as diabetes and reduction in excess weight, but it also involves more considerable potential complications and nutrient deficiencies, requiring lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation.
Let it be understood that the decision to opt for bariatric surgery should be made in direct consultation with your healthcare provider, taking into consideration your specific health conditions, obesity-related complications, and goals for weight loss. Learning extensively about these procedures' benefits and risks will serve as a tool for you and your healthcare provider to make the best decision together.
Choosing the Right Surgery and Post-Operative Care
Making the decision to undergo bariatric surgery is a significant step in your weight loss journey. A crucial part of this process is understanding which bariatric surgery option aligns best with your unique health status, weight loss goals, and potential risks. Additionally, realizing the importance of post-operative care, lifestyle changes, and sustained follow-up enables maintaining the health improvements and weight loss achieved through surgery.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Surgery Type
Choosing the right bariatric surgery requires careful consideration of various factors.
- Health Status: Existing health conditions can significantly influence the type of bariatric surgery that is appropriate for you. Patients with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), for instance, might benefit more from a roux-en-Y gastric bypass than a sleeve gastrectomy.
- Weight Loss Goals: Different surgeries have different expected weight loss outcomes. A sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass typically results in greater weight loss than adjustable gastric banding.
- Potential Risks and Complications: All surgical procedures come with inherent risks. Understanding these risks, considering your own risk tolerance, and discussing them with your healthcare team is a fundamental part of choosing the right bariatric procedure.
Importance of Post-Operative Care and Lifestyle Modifications
Post-operative care and lifestyle modification significantly impact the success of any bariatric surgery. Patients need to be aware that surgery is not an end in itself; instead, it's a tool to assist in weight loss, requiring significant lifestyle changes to be effective.
- Dietary Changes: Post-surgery, patients are typically placed on a clear liquid diet, gradually progressing to solid foods. Long-term, patients need to maintain a healthy, balanced diet, high in protein and low in fats and sugars.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of maintaining the weight loss achieved through surgery. The type and intensity of exercise might vary based on individual health status and surgeon's guidance.
- Mental Health Support: Psychological support, including counseling or support groups, is often beneficial to address feelings of anxiety, depression, or other body-image issues that can accompany drastic weight loss.
Long-Term Follow-Up and Support
Maintaining your new lifestyle post-surgery requires frequent follow-ups with your healthcare team and support groups.
- Medical Follow-Up: Regular check-ins with surgical and primary care teams are essential to monitor nutritional status, resolve any surgical complications, and ensure sustained weight loss.
- Support Groups: Peer support can provide motivation, offer practical advice, and promote healthy habits that contribute to long-term success post-surgery.
Bariatric surgery is a major decision that demands careful consideration and commitment. Your role in maintaining your weight loss journey does not end with the surgery but begins with it. Armed with the right knowledge and tools, you can make empowered decisions about the type of surgery, post-operative care, and long-term follow-up that best suits you.
In Summary
To summarize, bariatric surgery is a significant medical procedure designed to treat severe obesity levels, yielding potential benefits such as marked weight reduction and the improvement of related health conditions. Yet, this procedure is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It necessitates individuals to meet specific criteria, including a certain Body Mass Index (BMI) and a history of unsuccessful weight management attempts.
Bariatric surgery operates on restriction and malabsorption; that is, reducing the stomach's size or re-routing the digestive system to limit calorie absorption. Types of procedures include Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric band, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Each surgery varies with their respective advantages and potential shortfalls, necessitating careful consideration in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Post-operative care and the commitment to healthy lifestyle changes like dietary modulation, regular physical activity, and mental health support are equally crucial to ensure sustainable weight loss after surgery.
To put your knowledge into practice:
-
Assess the degree of your weight management struggle: Begin by honestly assessing your current state of health. If lifestyle modifications, diet, and exercise have not yielded the desired results, then consider the possibility of bariatric surgery.
-
Consult with your healthcare provider: Discuss potential weight-related health risks, your weight-loss goals, and surgery options with your healthcare provider. Understand the process, benefits, and risks involved in each of the surgical procedures.
-
Decide and prepare: Opt for the surgery that best fits your condition, needs, and goals. Begin preparation by adopting healthier dietary habits and regular physical activities, and mentally preparing for a lifestyle change.
-
Undergo Surgery: Once all preparations are complete, undergo the procedure under the guidance of your healthcare provider.
-
Adopt a healthy lifestyle post-surgery: Engage in a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintain mental health support.
-
Choose frequent follow-ups: Keep tabs on progress, nutritional status, and possible complications through regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider. Joining peer support groups can also provide motivation and advice for maintaining the new lifestyle.
Always remember, bariatric surgery is not a cosmetic process nor a quick-fix for obesity. Instead, it is, quite unequivocally, a catalyst towards facilitating healthier lifestyle changes. Be committed to making the transformation successful and sustainable through education, awareness, and a positive outlook.
